A reverse proxy service is an IP/Host, Port and Protocol combination that accepts client FTP/S, TCP (e.g. SFTP) or HTTP/S connection requests. To view existing reverse proxy services click on the Services node. A list of services are displayed.
Figure 2
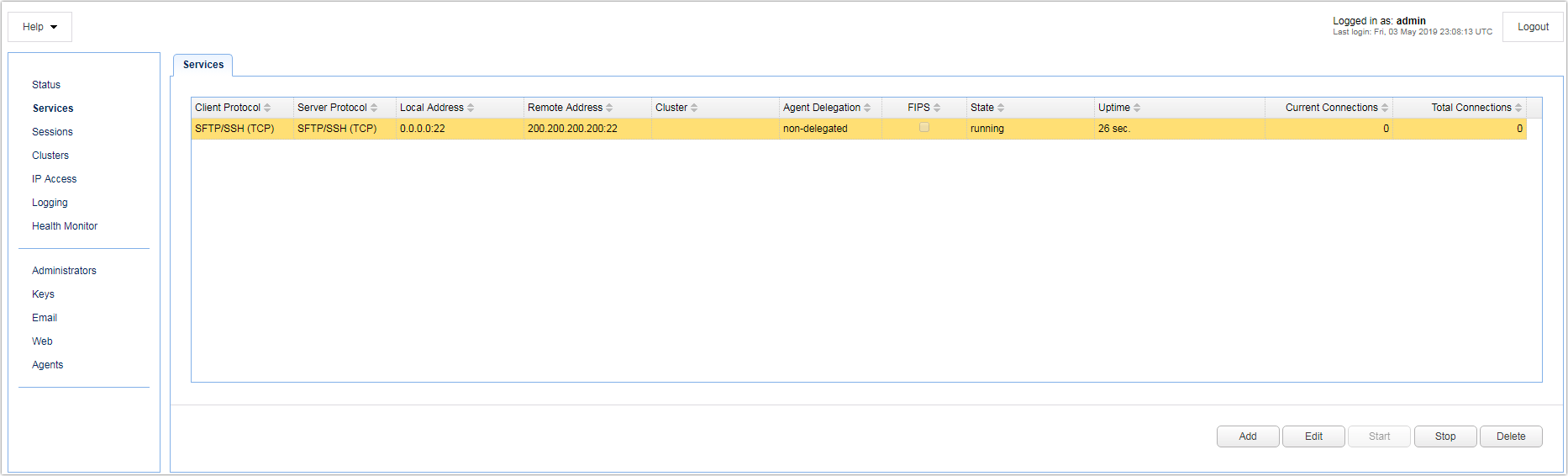
Client Protocol - The protocol used by the client to connect to the JSCAPE MFT Gateway Server. See Protocol types.
Server Protocol - The protocol used by the JSCAPE MFT Gateway Server to the remote host.
Local Host - The local IP that connections are accepted on.
Local Port - The local port that connections are accepted on.
Remote Address / Cluster - The remote host:port or cluster that connections are forwarded to.
Agent Delegation - Indicates whether connections are delegated to listening agents or handled by gateway directly.
State - The state of service (running, stopped).
Uptime - The total uptime since service start.
Current Connections - The current number of active connections.
Total Connections - The total number of connections since service start.
Buttons
Add - Click this button to add a new proxy service
Edit - Click this button to edit an existing proxy service
Start - Click this button to start a stopped proxy service
Delete - Click this button to delete an existing proxy service
Protocol types
Client protocol |
Server protocol |
Description |
FTP |
FTP |
Forwards standard unencrypted FTP connections |
FTP |
Implicit FTPS |
Forwards standard unencrypted FTP connections to a target encrypted Implicit SSL FTP service |
FTP |
SFTP |
Forwards standard unencrypted FTP connections to a target SFTP service |
FTPS |
FTP |
Forwards encrypted Implicit SSL FTP connections to a target standard FTP service |
FTPS |
FTPS |
Forwards both standard unencrypted FTP connections and encrypted explicit SSL connections using AUTH TLS or AUTH SSL client commands |
FTPS |
SFTP |
Forwards both standard FTP connections and encrypted FTPS connections to a target SFTP service |
Implicit FTPS |
FTP |
Forwards encrypted implicit SSL FTP connections to a target FTP service |
Implicit FTPS |
Implicit FTPS |
Forwards only encrypted implicit SSL FTP connections |
Implicit FTPS |
SFTP |
Forwards encrypted implicit SSL FTP connections to a target SFTP service |
HTTP |
HTTP |
Forwards HTTP connections to a target HTTP service |
HTTP |
HTTPS |
Forwards HTTP connections to a target HTTPS service |
HTTPS |
HTTP |
Forwards encrypted HTTPS connections to a target HTTP service |
HTTPS |
HTTPS |
Forwards only encrypted HTTPS connections |
TCP |
TCP |
Forwards connections without any protocol translation performed (Read and Write) |
TCP |
TCP/SSL |
Forwards SSL encrypted connections without any protocol translation performed (Read and Write) |
TCP/SSL |
TCP |
Forwards SSL encrypted connections to any TCP service |
TCP/SSL |
TCP/SSL |
Forwards SSL encrypted connections without any protocol translation performed (Read and Write) |
SFTP/SSH |
SFTP/SSH |
Forwards SFTP/SSH connections |
SMTP |
SMTP |
Forwards plain SMTP connections |
POP3 |
POP3 |
Forwards plain POP3 connections |
IMAP4 |
IMAP4 |
Forwards plain IMAP4 connections |
MySQL |
MySQL |
Forwards plain MySQL connections |
UDP |
UDP |
Forwards connections without any protocol translation performed (Read and Write) |
Add service
To add a service, click the Add button.
When the next screen appears, select the Client protocol and Server protocol. Click OK to proceed.
Figure 55
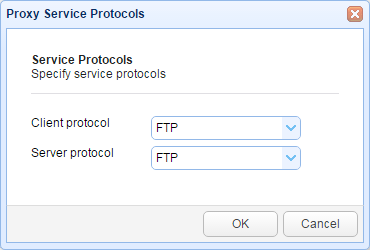
Figure 3
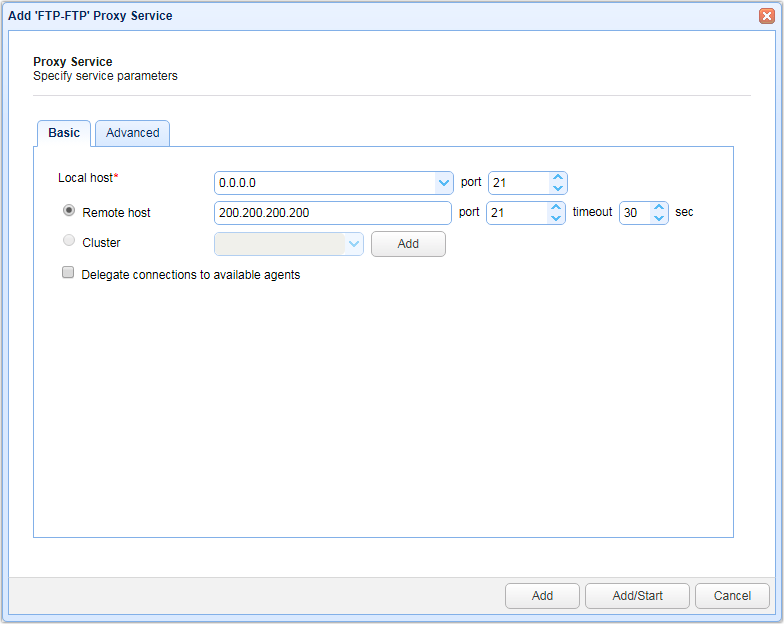
Configure the following settings:
Basic
Local host - The local IP that connections are accepted on.
Local port - The local port that connections are accepted on.
Remote host - The remote host/IP that connections are forwarded to.
Remote port - The remote port that connections are forwarded to.
Timeout - The maximum time in seconds before the reverse proxy times out when attempting to establish a connection with the remote service
Cluster - The cluster to forward connections to. This is used for load balancing purposes.
Delegate connections to available agents - If checked then connections will be handled by connected agents rather than by gateway directly.
Advanced
The contents of the Advanced tab will vary depending on the proxy service chosen.
FTP/S service Advanced settings
Figure 85

Command channel timeout (sec) - The time in seconds that a client may remain inactive on command channel before JSCAPE MFT Gateway forcefully disconnects it
Data channel timeout (sec) - The time in seconds that a client may remain inactive on data channel before JSCAPE MFT Gateway forcefully disconnects it
Data channel buffer size - The buffer size (in bytes) the OS will use in the socket when buffering data coming in from the network via the data channel
Data transfer buffer size - The buffer size (in bytes) that JSCAPE MFT Gateway will use when reading data from the socket
Passive IP - The IP address to use in response to passive client requests. (See Setting passive IP for FTP/S services)
Do not use Passive IP for client IP matching regex - Passive IP will not be used for clients connecting from IP matching the specified regular expression. This is useful in cases where you do not want internal users to have passive connection re-routed to an external IP address.
Passive port range - The passive port range to use in response to passive client requests. If not enabled a random port range will be used. Ensure that this port range is open on any firewall that may be in front of the gateway.
Ignore PASV/LPSV/EPSV IP of server host - Ignores the IP address returned by server when issuing PASV, LPSV or EPSV commands to server. Instead the IP address that gateway is connected to will be used. This is only applicable to FTP/S protocols.
Block bounce attack - If enabled FTP/S services will only be allowed to make PORT requests to originating host.
Block PASV attack - If enabled users will only be allowed to connect to passive data ports that are initiated by same client on command channel.
Shutdown server SSL - If enabled server must properly shutdown SSL connections for command channel when issuing CCC command.
Shutdown client SSL - If enabled client must properly shutdown SSL connections for command channel when issuing CCC command.
Enable FIPS compliance - This setting is not available in plain FTP. If switched ON, administrators will not be allowed to change allowed ciphers, whether through the GUI or administrative API. This setting is ideal for environments that need to comply with regulations requiring 'strong cryptography'. Many of these regulations only allow cryptographic algorithms recommended by duly recognized standards such as the Federal Information Processing Standards (FIPS).
SSL/TLS Ciphers - The SSL/TLS ciphers enabled for FTP/S services.
HTTP/S service Advanced settings
Figure 86
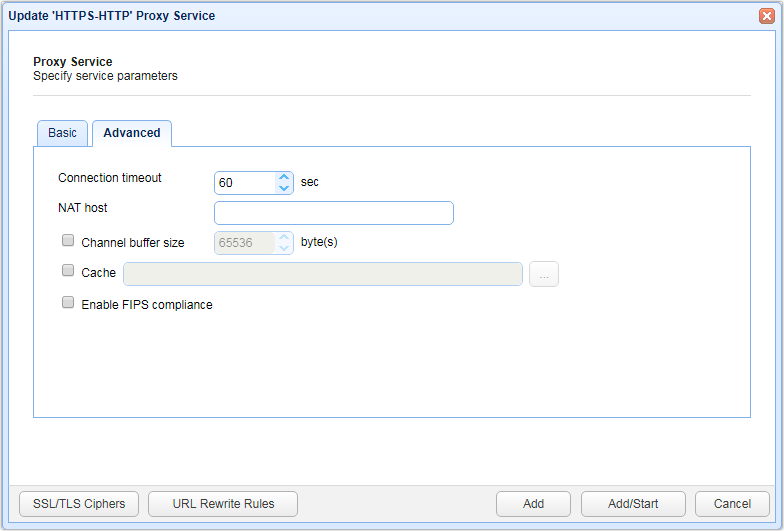
Connection timeout - The connection timeout for HTTP requests in seconds
NAT host - The hostname or IP address to be used if JSCAPE MFT Gateway is running on a server that uses NAT. See Setting NAT host...
Channel buffer size - The buffer size (in bytes) the OS will use in the socket when buffering data coming in from the network
Cache - The directory where the cache will be stored. See Caching HTTP/S content
Enable FIPS compliance - This setting is not available in plain HTTP. If switched ON, administrators will not be allowed to change allowed ciphers, whether through the GUI or administrative API. This setting is ideal for environments that need to comply with regulations requiring 'strong cryptography'. Many of these regulations only allow cryptographic algorithms recommended by duly recognized standards such as the Federal Information Processing Standards (FIPS).
TCP-based service Advanced settings
Figure 87
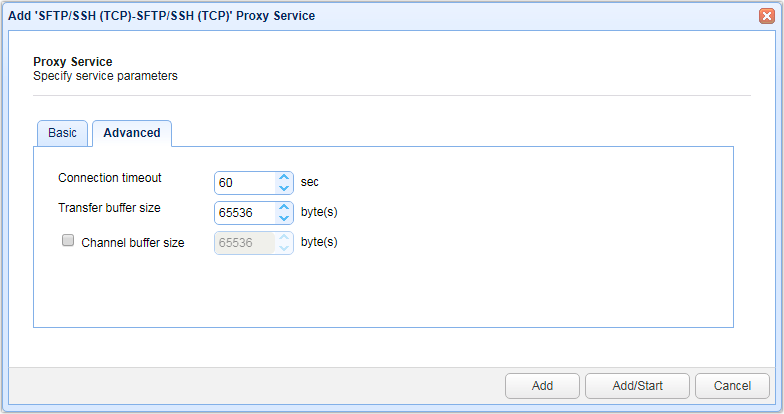
Connection timeout - The connection timeout for TCP requests in seconds
Channel buffer size - The buffer size (in bytes) the OS will use in the socket when buffering data coming in from the network
Transfer buffer size - The buffer size (in bytes) that JSCAPE MFT Gateway will use when reading data from the socket
UDP service advanced settings
Figure 88
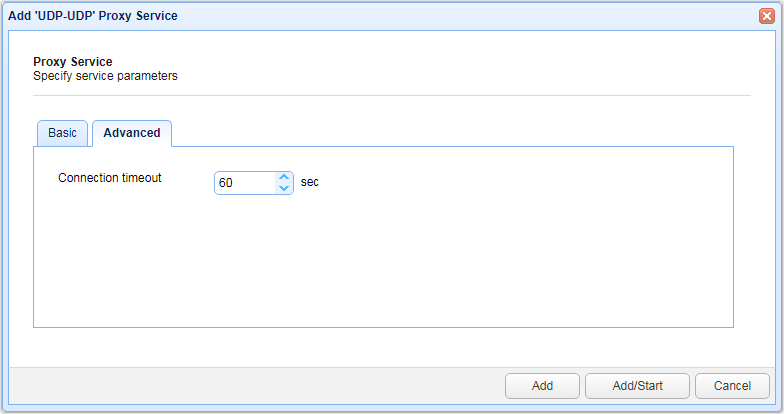
Connection timeout - The connection timeout for UDP requests in seconds
See also