JSCAPE MFT Server Web Client has all the common functions of a file transfer client without having to install file transfer client software on your end-users computers. All user permissions and virtual paths are observed when using JSCAPE MFT Server Web Client.
Figure 25
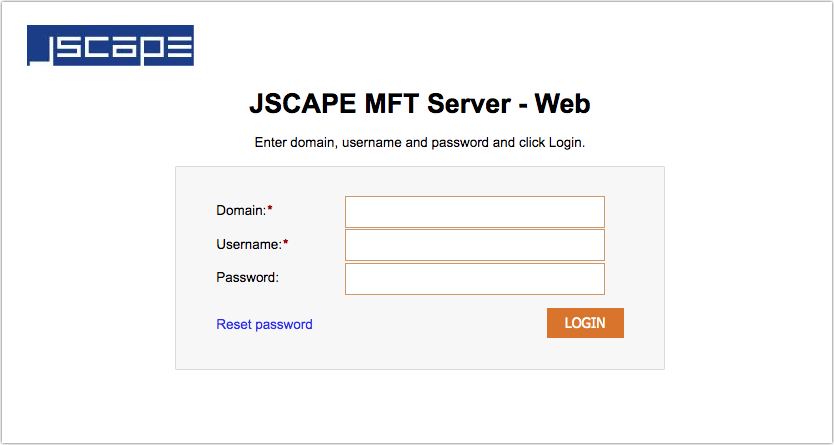
Domain - The name of the domain to connect to. This is the name of the domain as identified Domain Name column of JSCAPE MFT Server Manager, not the IP address or hostname although these may be the same.
Username - The account username.
Password - The account password.
Reset password - Allows user to reset lost password.
Figure 32

Figure 115

Personal Information
This section is available to all users and may be used to update the name, email address, company name, phone number, and password for a user account.
Public Key Authentication
This section can be used to generate a key pair for use in public key authentication (SFTP). When generating a key pair or importing a public key the public key is automatically placed in the .ssh/key.pub file relative to the users root login directory on the server. When generating a key pair the user is prompted to store the private key on their system. Note, private keys should never be stored on the server, except for purposes of connecting to other remote servers.
OpenPGP Encryption
This section can be used to generate an OpenPGP key pair for use in encrypting files uploaded to virtual directories.
Domain Administration
This section is only available to domain administrators and may be used to manage users.
Quotas
This section displays any bandwidth quota or directory monitor quota information for the user.
Contacts
This section can be used to manage contacts for use in ad-hoc file transfers.
Ad-Hoc Activity
This section can be used to manage ad-hoc emails sent by the user.
Drop Zones
This section shows drop zone information for the user.
See also