AnyClient already supports an experimental AFTP (Accelerated File Transfer Protocol), which allows you to transfer files over low latency networks. To connect via AFTP, navigate to the General panel, expand the drop-down list beside Connection Type, and select AFTP.
Figure 25
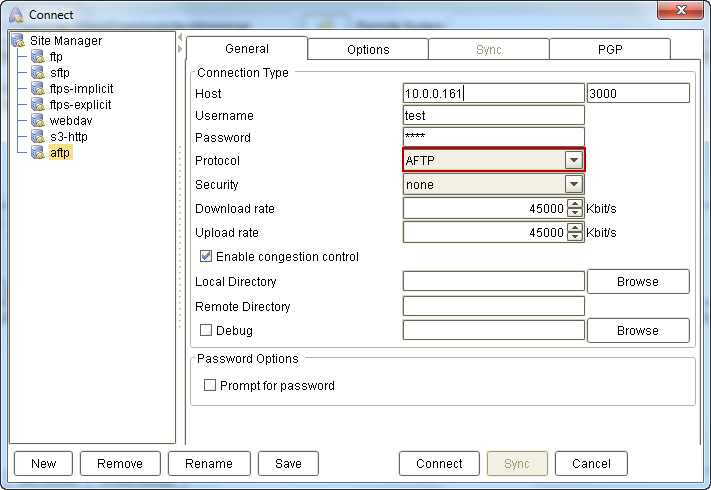
Note that the settings displayed on the dialog box will vary depending on which connection type you choose. So it is important that you select the Connection Type first before entering any setting values.
Basic AFTP
Unless you're behind a proxy, you'll only need to configure the following settings:
Host – This is the address of your server. (e.g. sampleftpsite.com). The small box you see beside the Host box is where you're supposed to enter the port number. In most cases, you can just leave it to the default: 3000.
Username – The username required for logging into the ftp site.
Password – The corresponding password for that username.
Security – If your server supports it, you may choose a security option for your data and credentials. The options are:
| • | None – no security. This is the default. |
| • | Credentials only – protect credentials only |
| • | Credentials and data – protect both credentials and data |
Download rate - The download rate in Kbit/s
Upload rate - The upload rate in Kbit/s.
Enable congestion control - Sets whether congestion control is enabled. If enabled transfer will begin at specified upload or download rate and adjust as needed for congestion. If disabled then congestion control will not be used and the specified upload or download rate will be used.
Once you've assigned the appropriate values to those settings, click the Connect button.
Figure 26
Assuming everything goes smoothly, the Connect dialog box will close and you'll be brought back to the home screen. Unlike when using other connection types, you may not see anything at the bottom of the home screen that would allow you to monitor the connection process of AFTP UDP/TCP. However, you will know you're already connected when the Remote System section activates.
Figure 18
Advanced AFTP settings
AFTP Compression
AFTP supports streaming compression which can increase throughput and file transfer speeds.
Enable – If checked compression is enabled, otherwise compression is disabled.
Exclude files with extension – A comma delimited, case-insensitive list of file extensions to exclude from compression. This defaults to a list of known file extensions which already utilize compression and that would not benefit from streaming compression.
Exclude files smaller than – The minimum file size in order to be considered for compression. The default is set to 10MB.
Proxy Settings
If you're having trouble connecting to a server from your office LAN, it's possible that a proxy server is in the way. Contact your network administrator and, after confirming that a proxy indeed exists, ask for the required proxy settings. These are the information you'll need:
Proxy Host – The address and port number for your proxy server. Enter the address into the bigger box and the port number into the smaller box.
Proxy Type – The default is NONE, whereby you don't need to specify any proxy settings. The other two options are SOCKS5 and HTTP. Choose one from the drop-down list.
Proxy User – This is the username required to connect to the proxy server.
Password – This is the corresponding password for that username.
PGP Decryption Settings
Enabled - If checked PGP encrypted files matching regular expression will be automatically decrypted after download.
Filename regex - The regular expression to use to determine whether files are PGP encrypted.
Private key - The private key to use for decrypting PGP encrypted files.
Password - The password protecting the private key.
Public key - The public key to use for verifying the signature on a PGP encrypted file.
Delete source - If checked PGP encrypted files will be deleted after successful decryption.