Mapping a network storage physical location (service/path) to a virtual path is a powerful feature that allows users to transparently access one or more remote services via a single client session.
In order to map a network storage physical path to a virtual path, first create the desired network storage type (ACCOUNTS > Network Storage)in the appropriate MFT Server domain. In the example below, the network storage configuration is for the MFT Server Agent protocol. This will be used as additional storage for the users that have been granted access to this network storage, either on the user-level or group-level, described below.
Figure 446
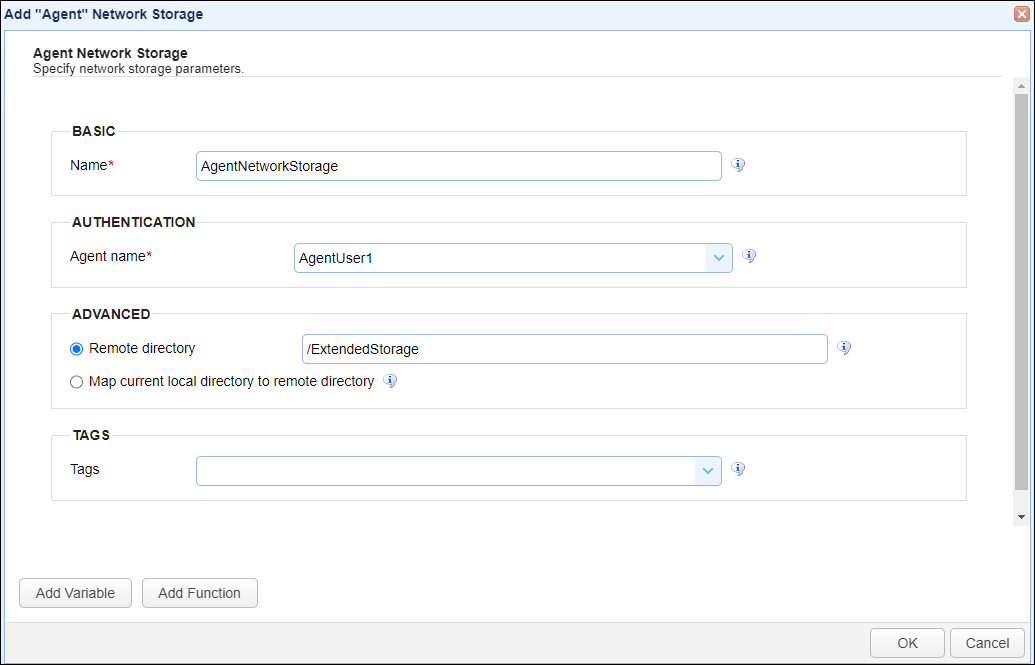
Next, map the network storage using a virtual path, where the virtual path is added via one of the options described below.
1) A user account (Accounts > Users > Users > <UserName>/Paths)
2) A user template (Accounts > Users > Templates > <TemplateName>/Paths), where the user connecting to the network storage was created using the template.
3) A group (Accounts > Groups > <GroupName>/Paths), where the user connecting to the network storage is a member of the group.
See the example below, which demonstrates how to add the virtual path on the user level.
Figure 447
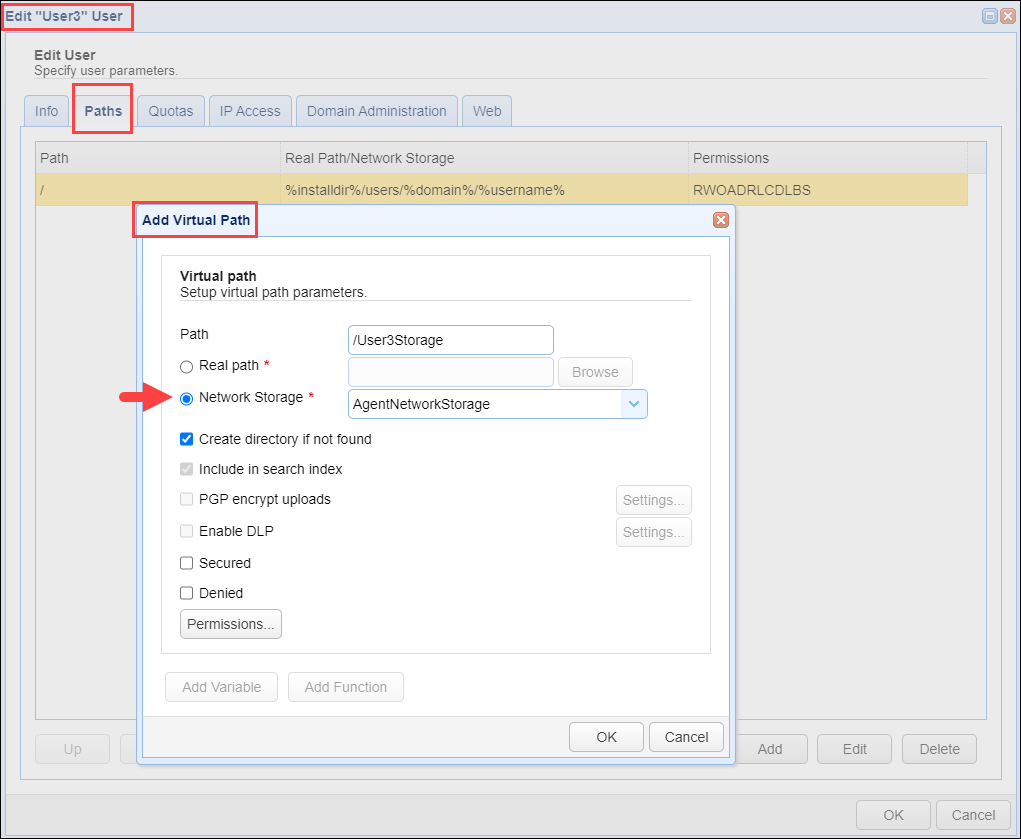
When users access the virtual path, for example, using the MFT Server Web Client UI, they will be connected to the remote service/storage solution when they select the virtual path (in the example above, the virtual path name is User3Storage). This is completely transparent to the end user, as they will only see the virtual path name in the Client UI.
See also