MFT Server logs all user activity to a log directory, or JDBC accessible database, or the system database. Each type is described below. To configure logging preferences go to the AUDIT > Logging module in MFT Server Manager for the desired domain.
Logs all server activity to a directory.
Figure 12
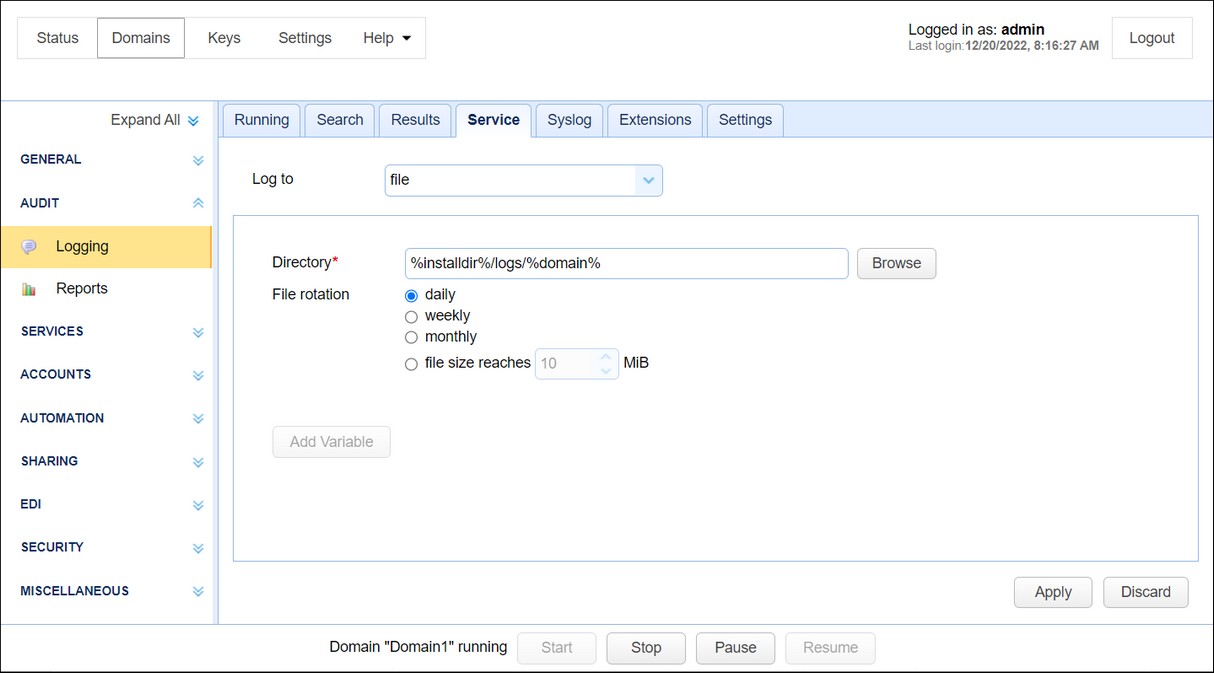
Directory - The directory where to store log files.
File rotation - The frequency in which to rotate log files.
Logs all server activity to a JDBC accessible database. To use the Database log option, you can opt to allow the system to create the database for you, or you can create the database and the necessary tables on your database server. If you wish to create the database yourself, example database schema for MySQL, Microsoft SQL Server and Oracle are provided in the files etc/mysql-log.sql, etc/mssql-log.sql, etc/oracle-log.sql, and etc/postgresql-log.sql respectively. The etc directory is found inside the MFT Server installation directory. Libraries for JDBC drivers must be placed in the libs/jdbc directory of your MFT Server installation, and the MFT Server Service must be restarted in order for the database to be accessible to MFT Server. Alternatively, you can populate the required fields, and click on the Create DB button, whereby the system will create the database for you.
Figure 63
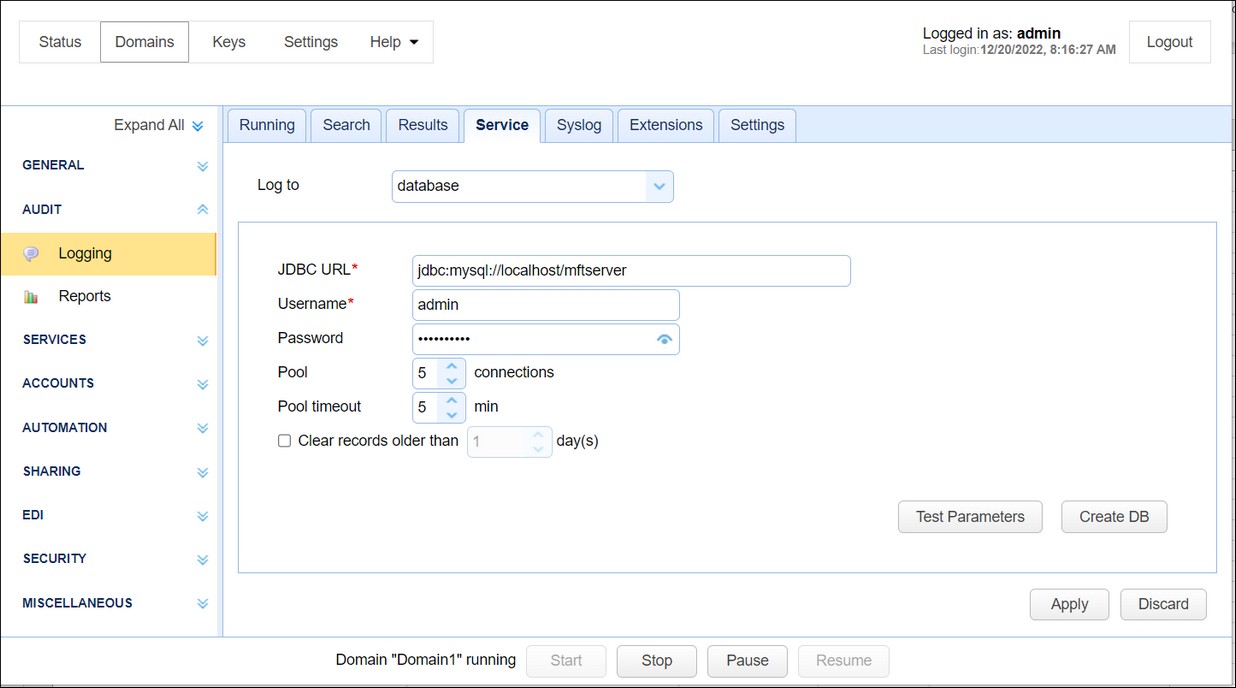
JDBC URL - The JDBC URL used to connect to the database. The above example demonstrates connecting to a MySQL database. Contact your database vendor for access to JDBC libraries and assistance on specifying the JDBC URL.
Username - The username to connect with when authenticating with database.
Password - The password to connect with when authenticating with database.
Pool - The maximum number of connections in database pool.
Pool timeout - The maximum amount of time in minutes that the database connection can live in the pool without activity.
Clear records older than [x] days - When ticked, MFT Server will clear records in the database logs when their age exceeds x number of days
Test Parameters - Tests database connection using the specified settings.
Create DB - If you click on this button, the system will create the logging database for you, based on the fields you entered.
Logs all server activity to the MFT Server system database. This means the system database and the user activity (for all domains) are all stored in the same database. This option is not supported if you are using the embedded (H2) database that comes bundled with MFT Server.
Logs all activity to a syslog daemon in addition to your existing File Log or Database Log settings. To use the Syslog option you must have an existing syslog daemon running. This may be a local or remote syslog daemon.
Figure 116
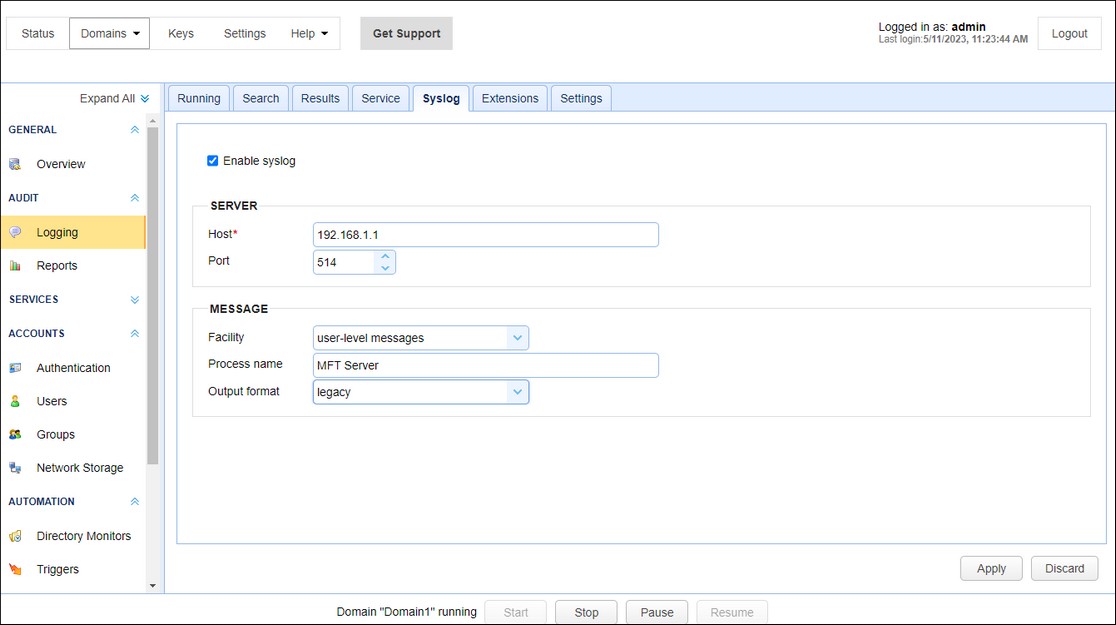
Host - The IP address of syslog daemon.
Port - The port of syslog daemon.
Facility - The syslog facility to use.
Process name - Process name tag to apply to all log messages sent to syslog daemon.
Output format - Legacy or raw. This field determines how the data will look when sent to syslog daemon. The legacy format is how the data was originally formatted, whereas raw is newer and uses a different format.
Logs all domain logging activity to a Splunk HTTP Event Collector (HEC). To use this option you must have a Splunk HEC installation. This option works in addition to your existing log settings configured within YourDomain > AUDIT > Logging > Service and YourDomain > AUDIT > Logging > Syslog (if enabled).
Figure 402
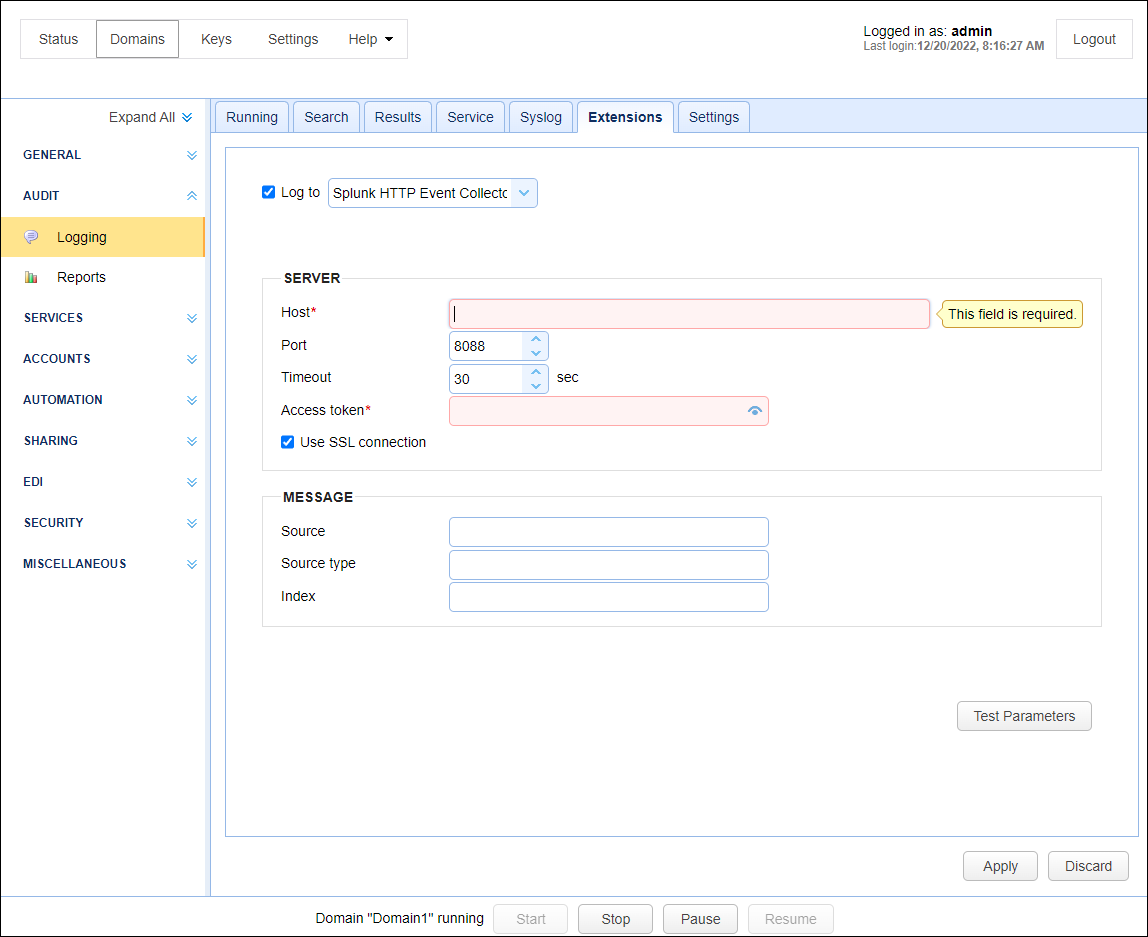
Log to - Splunk HTTP Event Collector. When checked, MFT server will stream domain-level logging data to a Splunk deployment.
Host - The IP or hostname of the Splunk Enterprise or Splunk Cloud Platform server.
Port - The port of the Splunk deployment. The default is 8088.
Timeout - The connection timeout, in seconds. The default is 30.
Access token - The token that is used by the MFT Server to authenticate the connection to Splunk HEC. Your Splunk administrator or a designated token administrator should generate and provide you with a valid token.
Source - The source value to assign to the event data. This typically identifies the application where the data is coming from (e.g. MFT Server).
Source Type - The source type value to assign to the event data. This typically identifies the type of data coming from the source. (e.g. Domain logs).
Use SSL Connection - When checked, an SSL connection is used to connect to the Splunk deployment.
Index - The name of the Splunk index.
Test Parameters - Click on this button to test the connection from the MFT Server to the Splunk deployment.
Note: If a failure occurs in logging the data to the Splunk HEC, you can be alerted about this condition using a Trigger with an Event type of Log Extension Failure.
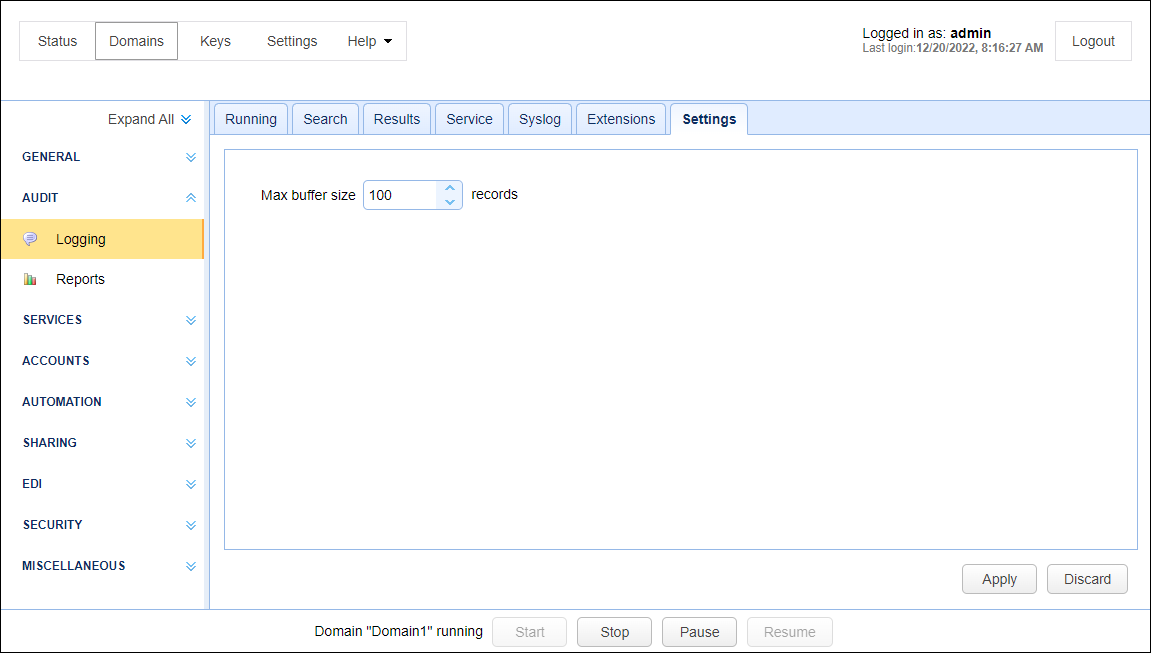
Max buffer size - Defines the maximum number of records that will be stored in the buffer
Figure 65
In the event that the database server cannot be contacted logging data will be directed to a temporary file located in the backup directory of your MFT Server installation. To move the contents of this temporary log file to your database use the js-backuplog command providing the domain that you wish to restore. The js-backuplog executable may be found in your MFT Server installation directory.
Example
js-backuplog -domain localhost
The above command moves the contents of the temporary log file for domain localhost to the log database assigned to this domain.